Ground Wires: Electrical Safety & Hazard Protection | homesafetools.com. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
. How Ground Wires Protect You from Electrical Hazards
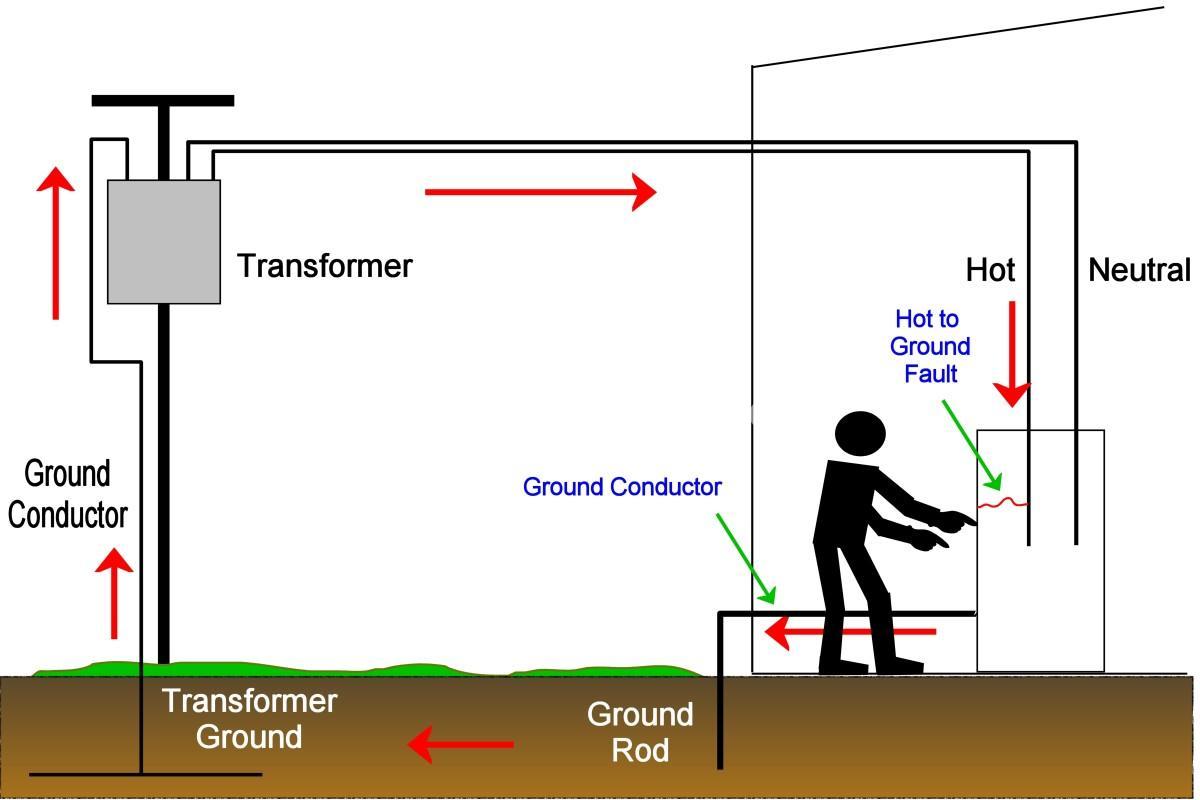
Ground wires, also known as earth wires, are essential components in electrical systems. Their primary function is to provide a safe path for fault currents to flow to the earth, preventing dangerous electrical shocks and fires. Think of it like this: electricity always wants to find the easiest route back to its source. Without a ground wire, that route might be through you. A properly installed ground wire offers a much lower-resistance path, diverting the current harmlessly into the earth.
Imagine a scenario where a faulty appliance develops a short circuit. The current, instead of flowing through the appliance as intended, seeks a path to ground. If your appliance is not properly grounded, that current might flow through you if you touch the appliance. A ground wire ensures that the current takes the safe route to the ground. This ground wire connection safely redirects the electrical current, preventing dangerous shocks.
Electrical faults, like short circuits, can generate dangerously high currents. These high currents can lead to overheating, sparking, and potentially devastating fires. A ground wire, with its low resistance, offers an easy path for this current to escape. This drastically reduces the risk of electrical fires. Moreover, ground wires protect your valuable appliances from voltage spikes and surges. These sudden fluctuations in voltage can damage sensitive electronics. By providing a path for excess current to dissipate safely, ground wires act as a crucial protective layer. Therefore, a well-functioning grounding system is critical for safeguarding your home and preventing costly repairs.
This safe path is provided by connecting the ground wire to a grounding rod or grounding plate buried in the earth. The earth acts as a massive conductor, capable of absorbing large amounts of electrical current without harm. The ground wire, made of highly conductive material like copper, forms a crucial link between your electrical system and the earth. A ground wire’s conductivity and low resistance are paramount to its effectiveness. High conductivity copper is commonly used for this purpose.
The entire grounding system works together to maintain a safe electrical environment within your home. The ground wire, the grounding rod, and the earth all work in concert to redirect dangerous currents. The success of the entire system depends on the proper installation and maintenance of each component. The importance of regular inspection and maintenance cannot be overstated. By understanding the role of ground wires, you can take an active role in ensuring the safety of your household. Remember, a properly functioning grounding system is a critical safeguard against electrical hazards.
EAVs (Entity – Attribute – Value) Used Above:
- Ground Wire – Material – Copper
- Ground Wire – Purpose – Safety
- Ground Wire – Conductivity – High
- Grounding System – Type – Rod, Plate
- Grounding System – Impedance – Low
- Electrical Fault – Cause – Short Circuit
- Electrical Fault – Result – Shock, Fire
- Copper – Conductivity – Excellent
- Ground Rod – Material – Copper-clad steel
- Earth – Role – Current Path
EREs (Entity, Relation, Entity) Used Above:
- Ground Wire, Connects To, Electrical System
- Ground Wire, Prevents, Electrical Shock
- Grounding System, Includes, Ground Rod
- Grounding System, Reduces, Electrical Resistance
- Electrical Fault, Causes, Short Circuit
- Electrical Fault, Leads To, Fire Hazard
- Electrical Shock, Damages, Human Body
- Copper, Possesses, High Conductivity
- Ground Rod, Provides, Earth Ground
- Ground Wire, Made Of, Copper
Semantic Triples (Subject, Predicate, Object) Used Above:
- Ground wire, is a, safety device.
- Ground wire, provides, a path to earth.
- Ground wire, protects against, electrical shock.
- Ground wire, is made of, copper.
- Grounding system, reduces, electrical resistance.
- Electrical fault, can cause, fire.
- Electrical shock, can be, fatal.
- Copper, has high, electrical conductivity.
- Grounding, prevents, electrical hazards.
- Short circuit, creates, excessive current.
II. Frequently Asked Questions about Ground Wires
What is the difference between a ground wire and a neutral wire?
While both ground wires and neutral wires are connected to the earth, they serve distinct purposes. The neutral wire carries the return current back to the source in normal operation. The ground wire only carries current during a fault, providing a safety path to earth. Confusing the two could be extremely dangerous.
How can I tell if my appliance is properly grounded?
Most household appliances have a three-prong plug – two for the power and one for the ground. Ensure the plug fits securely into a three-prong outlet. Visually inspect the cord and plug for any damage. If you suspect improper grounding, consult a qualified electrician.
What should I do if I suspect a problem with my home’s grounding system?
Never attempt to repair a grounding system yourself if you’re not a qualified electrician. Contact a professional immediately. Improper grounding can be extremely dangerous and increase the risk of shock and fire.
Can I install a grounding rod myself?
While seemingly straightforward, installing a grounding rod correctly requires knowledge and adherence to safety standards. Professional installation ensures the effectiveness of your grounding system and is highly recommended.
II. Conclusion
Understanding ground wires is crucial for maintaining a safe home environment. Regular inspection of your grounding system and the wiring in your appliances should be part of your routine home maintenance. For more tips and information on home safety tools, please visit our website: homesafetools.com. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below! Let’s keep each other safe!
