Safe Circuit Breaker Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
. Essential Safety Precautions: Before You Begin
First things first: safety! Before even thinking about touching a wire, you absolutely must prioritize safety. This isn’t a casual DIY project; electricity is dangerous. Therefore, the first step in any circuit breaker installation is completely shutting off the power to the electrical panel. This is non-negotiable. You’ll find the main breaker, usually labeled clearly, and flip it to the “off” position. However, don’t just rely on that. Next, get a non-contact voltage tester – a truly essential piece of equipment for anyone working with electricity – and thoroughly check every wire connected to the area where you’ll be working. You absolutely want to be sure the power is off before you start. This step is so important that I can’t stress it enough.
Moreover, you must use the proper Personal Protective Equipment, or PPE. This includes insulated gloves to protect your hands from electrical shocks, safety glasses to safeguard your eyes from any debris or sparks, and non-conductive footwear to isolate you from the ground, thus protecting you from any electrical current that might leak. Think of PPE as your armor against potential hazards. Neglecting PPE is simply reckless. Remember: it’s always better to be over-prepared than under-prepared when dealing with electricity.
(Entity – Attribute – Value) Examples:
- (Safety Gear, Type, Insulated Gloves)
- (Safety Gear, Type, Safety Glasses)
- (Power Shutoff, Method, Main Breaker)
- (Voltage Tester, Purpose, Verify Power Off)
(Entity-Relation-Entity) Examples:
- (Person, USES, Voltage Tester)
- (Voltage Tester, VERIFIES, Power Status)
- (Power Shutoff, PREVENTS, Electrical Shock)
- (Safety Gear, PROTECTS, Electrician)
(Subject-Predicate-Object) Examples:
- (Power Shutoff, IS, Crucial)
- (PPE, IS, Essential)
- (Voltage Tester, INDICATES, Power Absence)
- (Safety, REQUIRES, Careful Procedure)
Next, let’s gather the tools and materials you’ll need. You’ll want a good quality Phillips head screwdriver, a flathead screwdriver, wire strippers, a wire connector, and of course, the new circuit breaker itself. Remember to buy the correct amperage for your needs. You will need the proper gauge wiring too. Getting the wrong size wire is a common mistake, and it can be unsafe. It is recommended that you look up the correct wiring gauge based on the circuit breaker’s amperage.
Now, let’s move on to the installation itself. First, carefully open the electrical panel – which is often called a breaker box – and identify an empty space for your new circuit breaker. Make sure you’ve already turned off the power!
Once you’ve carefully chosen your slot, prepare the wires. Strip the insulation from the ends of the wires, making sure not to damage the copper. Connect the hot, neutral, and ground wires to the correct terminals on the new circuit breaker, matching colors accurately (often black, white, and bare copper or green). Always make sure the wire is securely attached. Loose connections can cause problems and lead to electrical hazards.
Next, carefully push the new circuit breaker into the panel and snap it into place. Make sure it is snug and secure. Then, carefully organize and tuck in the wires. Remember that you want to have good organization to minimize the risk of shorts. Once that’s complete, turn the power back on – slowly and carefully, again. Check if the circuit breaker is functioning correctly, for example, if you are testing the lighting circuit, check to see if the lights are on.
III. Tools and Materials Needed for the Job
Here’s a breakdown of the tools and materials you’ll need:
Essential Tools:
- Screwdrivers: Both Phillips head and flathead are essential.
- Wire Strippers/Cutters: For safely preparing the wires.
- Voltage Tester: A non-contact voltage tester is crucial for safety.
- Wire Connectors: To securely join wires.
- Level: To ensure the electrical panel is level. Sometimes useful for breaker installation.
Necessary Materials:
- Circuit Breaker: The correct amperage and type are critical.
- Wiring: The appropriate gauge of wiring is essential for safety and proper function. Make sure to follow the local electrical code.
- Wire Nuts/Connectors: For secure wire connections.
I can’t stress enough that selecting the correct tools and materials is paramount. Using the wrong ones can lead to unsafe installations and potential electrical issues down the road. The correct amperage rating for the circuit breaker is probably the most important thing you need to choose correctly. You must make sure this matches the existing home electrical installation wiring and the appliances that you are planning to connect to the circuit.
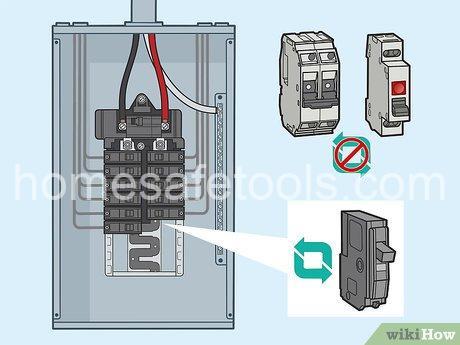
IV. Step-by-Step Circuit Breaker Installation Guide
The following steps provide a detailed guide to installing a circuit breaker:
- Prepare the Electrical Panel: Always remember to turn off power at the main breaker before working with the electrical panel. Inspect the panel for any available spaces. You might need a fish tape if you are installing a new circuit and need to pull a new run of wire through the walls.
- Wiring the Circuit Breaker: Strip the wire insulation carefully. Make sure to carefully match the colours of the wires (usually black for hot, white for neutral, and bare copper or green for ground). Connect each wire to its corresponding terminal on the circuit breaker. Tighten the screws securely.
- Installing the Circuit Breaker: Carefully insert the circuit breaker into its designated slot in the electrical panel and ensure it is firmly secured.
- Post-Installation Checks: Double-check all wire connections for tightness and ensure all wires are neatly organized.
Remember, each step is equally important; even a small mistake can have significant consequences. Take your time, follow the instructions carefully, and if you’re uncertain about any step, consult a qualified electrician. Safety should always be your top priority.
V. Testing the New Circuit Breaker
Once the installation is complete, it’s crucial to test the new circuit breaker. This involves turning the main power back on—cautiously—and then testing the circuit to which the new breaker is connected.
Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the outlets or light fixtures connected to the new circuit. If the voltage readings are correct and the breaker doesn’t trip under load, the installation was likely successful. However, if the breaker trips immediately or doesn’t provide power, there might be a problem with the installation or the circuit itself. In such cases, don’t hesitate to consult an electrician.
Safety testing is part of every job when dealing with electricity. Never skip this step.
VI. Different Types of Circuit Breakers
There are several types of circuit breakers, each with a specific function:
- GFCI Breakers: These are essential for safety in areas where water is present (bathrooms, kitchens). They protect against ground faults, which can cause electrical shocks.
- AFCI Breakers: These protect against arc faults, which are electrical arcs that can cause fires. They are often required in bedrooms.
- Double-Pole Breakers: These control two circuits simultaneously and are often used for larger appliances or multiple outlets.
- Single-Pole Breakers: These control one circuit and are the most common type of breaker used in homes.
Understanding the differences between these types of breakers is crucial for making informed choices during installation and ensuring proper electrical safety in your home.
VII. Important FAQs about How to Install a Circuit Breaker?
What are the most common mistakes when installing a circuit breaker?
Common mistakes include incorrect wire connections, loose connections, incorrect amperage selection for the circuit breaker, and neglecting essential safety precautions. Always double-check your work, paying particular attention to wire connections and ensuring the breaker is properly secured.
Do I need a permit to install a circuit breaker?
Local building codes vary, so check with your local authority to determine whether a permit is required. Installing a circuit breaker incorrectly can lead to severe problems or even accidents, so it’s extremely important to follow these guidelines as best as possible.
Can I install a circuit breaker myself, or should I hire an electrician?
While it is possible to install a circuit breaker yourself if you have the appropriate skills and experience, it’s highly recommended to hire a licensed electrician, especially if you are uncomfortable working with electricity or unsure of any part of the process. Safety comes first.
What tools and materials do I need for circuit breaker installation?
You’ll need the correct circuit breaker for your needs, appropriate gauge wire, screwdrivers, wire strippers/cutters, a voltage tester, and wire connectors. The correct size and amperage of the circuit breaker is vital.
What should I do if the circuit breaker keeps tripping?
If the circuit breaker keeps tripping, it indicates an overload on the circuit. Unplug unnecessary appliances or devices connected to the circuit to reduce the load. If the problem persists, contact a qualified electrician.
VIII. Conclusion
Installing a circuit breaker correctly is vital for maintaining the safety of your home’s electrical system. Remember always to prioritize safety and consult a qualified electrician when in doubt. For more tips and resources on home safety tools, visit https://homesafetools.com. Share your experiences and ask any questions in the comments below! Happy and safe DIY-ing! This article is courtesy of John Amrry.
