Three-Phase Electrical Systems: Basics, Advantages & Safety. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
nderstanding the Basics of Three-Phase Systems
Let’s start with the fundamentals. You’re probably familiar with single-phase AC power, which is what powers most household appliances. Now imagine that instead of one wave of electricity, you have three! That’s the core of a three-phase electrical system. These three waves, or phases, are precisely 120 degrees apart. Think of it like a three-legged stool – much more stable than a one-legged one! This offset is crucial because it allows for a more efficient and powerful delivery of electricity. It’s like having three separate streams of electricity working together, instead of just one.
This setup is achieved using a generator or alternator, which uses rotating magnets to induce an electric current in three separate sets of coils. Each coil generates one of the three phases. This creates three separate but synchronized alternating current (AC) waveforms. Because they’re offset, the overall power output is smoother and more consistent than with a single-phase system. This is especially important in industrial applications where heavy machinery demands a constant power supply. The difference is like the smooth, consistent flow of a river compared to the erratic bursts of a small stream.
The significance of this design lies in the way power is delivered. Unlike single-phase systems which rely on one path for electricity, three-phase systems leverage three separate lines, leading to increased efficiency and reduced material use. You see, with three-phase, the current flows more consistently, reducing energy loss in the wires – a big advantage, especially for long-distance transmission. It’s considerably more efficient, hence why it’s the backbone of industrial and commercial power grids worldwide.
The way these phases interact is also important to understand. Line-to-line voltage refers to the voltage between any two phases, while line-to-neutral voltage (in a wye configuration) is the voltage between one phase and a neutral point. These voltages are related mathematically, a key factor in designing and implementing three-phase systems. Without getting too technical, this relationship is what makes three-phase power so remarkably efficient and powerful.
Advantages of Three-Phase Power
Several key advantages make three-phase systems superior to their single-phase counterparts. Firstly, they boast a higher power-to-weight ratio. This means that for the same amount of power delivered, you need significantly less copper wire and therefore lighter infrastructure. This translates into substantial cost savings, both in initial investment and ongoing maintenance. Less material is needed because the current flow is distributed more evenly across the three lines; it’s like spreading the workload amongst three people versus one.
Secondly, three-phase systems are incredibly efficient in power transmission and distribution. The balanced nature of the three phases reduces energy losses during transmission, leading to less wasted energy and a smaller carbon footprint. This efficiency is vital for long-distance power transmission, making it the preferred method for large-scale projects.
Moreover, the consistent power delivery of three-phase leads to smoother operation in motors and other machinery. Reduced vibrations and noise are direct results, making workplaces safer and quieter. This smooth and constant power is essential for many high-power devices, leading to prolonged equipment lifespan. This is particularly valuable in factories where machinery operates 24/7.
Finally, three-phase power is exceptionally cost-effective for large-scale applications. While the initial setup might seem more complex, the long-term savings from increased efficiency and reduced energy losses far outweigh the investment. This makes it the preferred choice for both industrial applications and large commercial buildings.
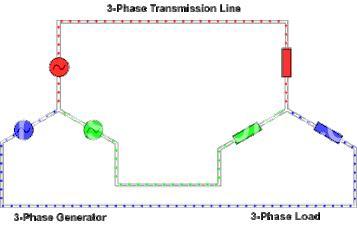
Three-Phase System Configurations
Now let’s explore the two primary configurations for three-phase systems: Wye (Y) and Delta (Δ). The Wye configuration connects the three phases to a common neutral point, offering both line-to-line and line-to-neutral voltages. Think of it as a star formation. The Delta configuration, on the other hand, connects the three phases in a closed loop, forming a triangle. This setup simplifies installations in certain scenarios, making it a popular option in many applications. The choice between these two depends heavily on the specific requirements of the application. For instance, the Wye configuration is commonly used for larger power distribution systems while the Delta configuration is often preferred for motor loads.
The differences between the two configurations become more apparent when looking at voltage and current relationships. Understanding these relationships is crucial for proper system design and troubleshooting. It’s like knowing the inner workings of a clock; understanding each component’s role helps in identifying and fixing any malfunctions. Each configuration’s features affect efficiency, voltage regulation, and fault tolerance, aspects critical for different contexts.
Choosing between Wye and Delta depends heavily on factors like the load characteristics, voltage levels, and the overall system requirements. Careful consideration of these aspects is vital for optimal system performance.
Common Applications of Three-Phase Systems
Three-phase power isn’t just a technical detail; it’s the lifeblood of our modern world. You’ll find it powering everything from large industrial motors to the electrical grids that supply electricity to your homes. Large manufacturing plants depend heavily on three-phase power to run their production lines, which incorporate numerous heavy-duty machines. The smooth, consistent power delivery ensures optimal performance and longevity of these machines.
In high-rise buildings and large commercial complexes, three-phase power supplies various equipment, from elevators and air conditioning units to lighting systems. Hospitals, data centers, and other institutions with high power demands also rely heavily on three-phase systems to ensure reliable and uninterrupted operation. Consider the electrical requirements of a hospital’s MRI machines or the servers in a massive data center, and you can appreciate the importance of a three-phase power supply.
Electric trains and trams also leverage the efficiency and power of three-phase technology for their propulsion systems. The consistent power supply ensures reliable and efficient operation of these mass transit systems.
Comparing Three-Phase and Single-Phase Systems
Let’s look at a simple comparison to highlight the key differences. Single-phase is generally used for residential purposes and smaller-scale applications, while three-phase excels in high-power scenarios due to its greater efficiency and reliability. The power delivery in a three-phase system is far more consistent and less prone to fluctuations compared to single-phase, making it ideal for operating heavy-duty machinery without the risk of sudden voltage drops.
| Feature | Single-Phase System | Three-Phase System |
|---|---|---|
| Power Delivery | Less efficient, prone to fluctuations | More efficient, smoother delivery |
| Applications | Residential, low-power applications | Industrial, commercial, high-power |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but lower long-term costs |
| Voltage | Typically 120V or 240V | Higher voltage levels |
| Wire Requirements | More wire required for same power | Less wire required for same power |
Safety Precautions When Working with Three-Phase Systems
Working with three-phase power can be extremely dangerous due to the higher voltage levels involved. Always prioritize safety. Never attempt to work on a three-phase system unless you’re a qualified electrician with proper training and experience. Ignoring this can lead to serious injury or even death.
Always use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including insulated tools and safety gloves. Before starting any work, ensure the power is completely disconnected and locked out using proper lockout/tagout procedures. This prevents accidental energization and protects you from electrocution. It’s essential to treat these systems with utmost respect, as a single mistake can have devastating consequences.
FAQs about Three-Phase Electrical Systems
What are the main differences between single-phase and three-phase power systems?
The primary difference lies in the number of phases and the way power is delivered. Single-phase provides a single alternating current waveform, while three-phase uses three, each 120 degrees out of phase. This difference translates to increased efficiency and power capacity in three-phase systems, making them suitable for higher-power applications.
How is three-phase power generated?
Three-phase power is generated using an alternator with three separate windings spaced 120 degrees apart. As the rotor spins, it induces an alternating current in each winding, creating three distinct phases.
What are the common configurations of three-phase systems?
The two main configurations are Wye (Y) and Delta (Δ). The Wye configuration connects the three phases to a neutral point, while the Delta configuration connects them in a closed loop. The choice of configuration depends on factors like voltage requirements and load characteristics.
What are some safety precautions to take when working with three-phase power?
Three-phase systems operate at high voltages, presenting significant electrocution risks. Always ensure proper lockout/tagout procedures are in place before working on them. Use insulated tools and protective equipment, and only qualified electricians should handle these systems.
What are the typical applications of three-phase electrical systems?
Three-phase systems are extensively used in industrial settings for powering heavy machinery, motors, and large equipment. They are also common in commercial buildings and power grids due to their efficiency and power delivery capabilities.
Conclusion
Understanding three-phase electrical systems is crucial for anyone involved in electrical work, from home enthusiasts to industrial professionals. Remember, safety always comes first! Want to learn more about home safety? Leave a comment, share this post, or check out more articles at https://homesafetools.com. Thanks for reading! John Amrry, homesafetools.com.
