How Do Transformers Work? Voltage Transformation & Components Explained. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
nderstanding the Basic Principles of Voltage Transformation
Let’s start with the fundamentals. Voltage is the electrical potential difference, essentially the “push” that moves electrons through a circuit. It’s measured in volts. A higher voltage means more electrical pressure. Now, why is this important for transformers? Because transformers are all about changing this voltage! They don’t create electricity; they cleverly modify existing alternating current (AC).
AC electricity, unlike direct current (DC), constantly changes direction. This fluctuating current is key to how transformers operate. Imagine a wave—that’s what AC looks like. This constant change is what creates the electromagnetic induction that makes transformers work.
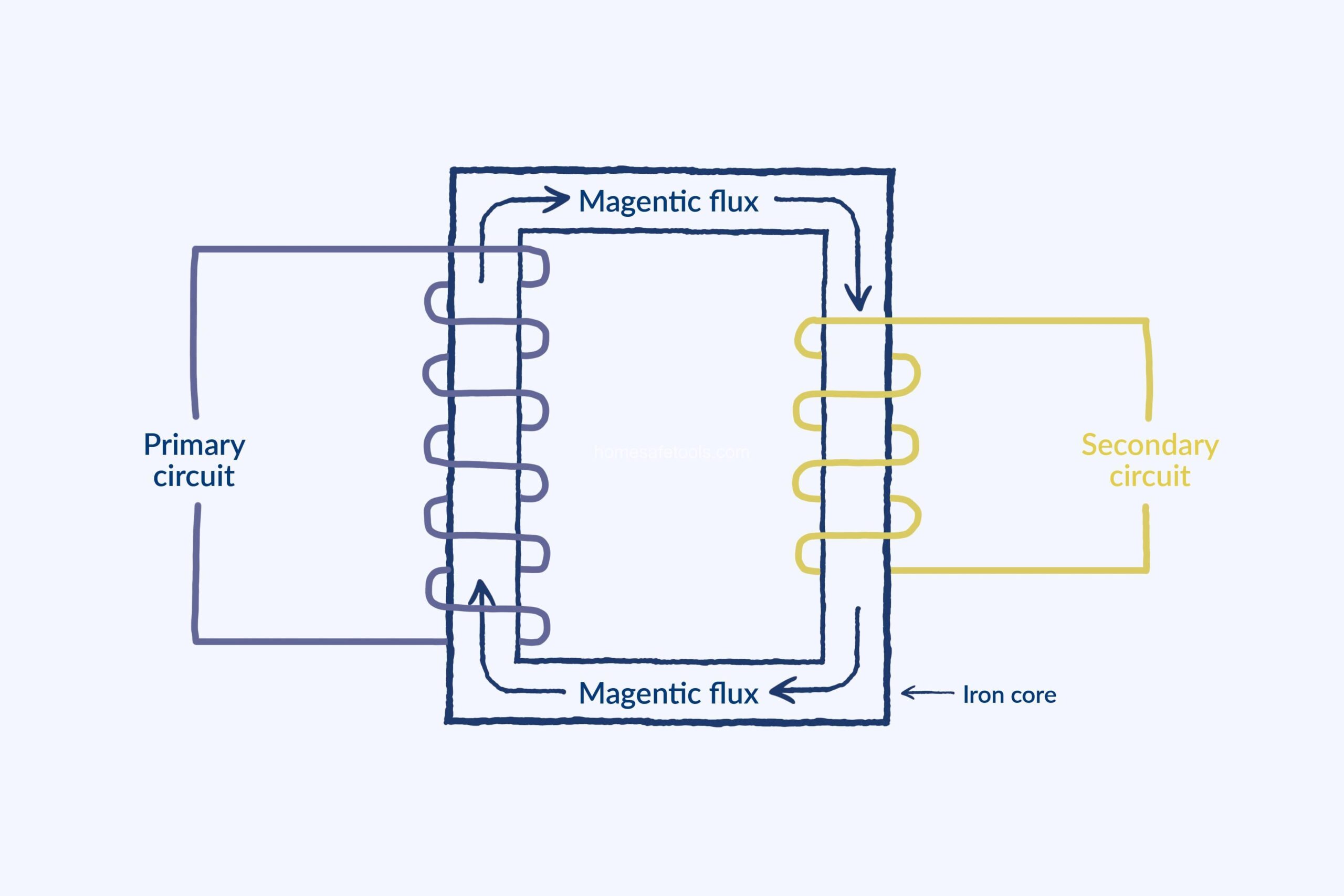
Electromagnetic induction is based on Faraday’s Law. Simply put, changing magnetic fields create electricity. A transformer uses this principle brilliantly. The primary winding, when fed with AC, generates a fluctuating magnetic field. This field then interacts with the secondary winding, inducing a voltage within it. This induced voltage can be higher or lower than the input voltage, depending on the design of the transformer – hence, step-up and step-down transformers. This is the core concept behind the entire process. It’s all about clever manipulation of magnetic fields to control the flow of electricity.
The core itself plays a crucial role. It’s usually made of laminated iron or ferrite, materials that easily conduct magnetic fields. This core channels the magnetic flux, making sure most of the field generated by the primary winding reaches the secondary winding efficiently. Without the core, much of the magnetic field would be lost, making the transformer inefficient. Different core designs (like toroidal and E-I cores) exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
Transformer Components and Their Functions
Let’s take a closer look at the individual parts. We’ve got the primary winding, connected to the input AC voltage source. The number of turns (coils) in this winding is crucial; more turns mean a stronger magnetic field. Then there’s the secondary winding, connected to the output circuit. Again, the number of turns here dictates the output voltage.
Imagine the primary and secondary windings like two interconnected buckets. The primary bucket receives water (electricity), and through a clever mechanism, it makes the second bucket fill up with either more or less water than it received. This is the essence of voltage transformation.
The relationship between the number of turns in the primary (Np) and secondary (Ns) windings is essential. The voltage ratio is directly proportional to the turn ratio: Vp/Vs = Np/Ns. More turns on the secondary winding mean a higher output voltage (step-up transformer), and fewer turns mean a lower output voltage (step-down transformer).
Furthermore, remember that there’s an inverse relationship between voltage and current. Step-up transformers increase voltage but decrease current, while step-down transformers do the opposite. The power remains roughly constant (ignoring losses), so increasing one parameter reduces the other.
How a Step-Up Transformer Increases Voltage
A step-up transformer increases voltage. This is achieved by having more turns in the secondary winding compared to the primary winding. When AC current flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field that is amplified by the transformer core, and this field induces a higher voltage in the secondary winding. This is how you get a higher voltage output than input, which is critical for applications like power transmission over long distances. The increased voltage reduces power loss during transmission.
How a Step-Down Transformer Decreases Voltage
Conversely, a step-down transformer decreases voltage. Here, the secondary winding has fewer turns than the primary winding. The process remains similar; the changing magnetic field induced by the primary current generates a voltage in the secondary winding, but this time, the resulting voltage is lower. Step-down transformers are essential in household applications, transforming the high voltage from power lines to the lower voltage needed for household appliances and electronics.
Different Types of Transformers and Their Applications
There are several types of transformers tailored to specific applications. Besides step-up and step-down transformers, we have isolation transformers. These transformers isolate the input circuit from the output circuit electrically. This is crucial for safety, particularly in environments where electrical grounding might be unreliable. They prevent electrical shocks by separating the input and output circuits even when the voltages are the same.
Another important type is the autotransformer. Unlike a regular transformer with completely separate primary and secondary windings, an autotransformer has a single winding that serves as both primary and secondary. This design makes them more compact and efficient for certain applications, though they lack the complete electrical isolation of isolation transformers.
Transformer Efficiency and Losses
While the theory is simple, real-world transformers aren’t perfect. Losses arise due to several factors. Copper losses (also known as I²R losses) occur due to resistance in the windings. Think of it as energy lost as heat in the wires. Then there are iron losses – hysteresis losses and eddy current losses within the core. These are losses due to the core’s magnetization and the generation of small currents within the core material itself. These losses reduce the efficiency of the transformer.
Safety Considerations When Working with Transformers
Safety is paramount when dealing with transformers, especially those operating at high voltages. High voltages can be lethal, so always treat them with respect and care. Never work on live transformers unless you’re properly trained and equipped. Short circuits can quickly lead to overheating, fire, and other hazards. Always ensure proper grounding and use appropriate protective equipment. Finally, dispose of transformers responsibly. Their internal components can contain hazardous materials, which must be handled appropriately.
What are the main components of a transformer?
A transformer has three main parts: the primary winding, the secondary winding, and the core. The primary winding receives the input voltage, the secondary winding provides the output voltage, and the core channels the magnetic flux between the windings, making the energy transfer efficient.
How does a transformer change voltage?
Transformers utilize the principle of electromagnetic induction. An alternating current in the primary winding creates a fluctuating magnetic field in the core. This field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, the magnitude of which depends on the ratio of the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings.
What is the difference between a step-up and a step-down transformer?
A step-up transformer increases voltage, and this is achieved by having more turns in the secondary winding compared to the primary winding. Conversely, a step-down transformer reduces voltage. This happens when there are fewer turns in the secondary winding than in the primary winding.
What are the common types of transformers?
Common transformer types include step-up, step-down, and isolation transformers. An autotransformer is also notable for its unique single winding design. Each type serves different purposes, from power transmission to safe operation of electronic devices.
What are the efficiency limitations of transformers?
Real-world transformers aren’t perfectly efficient due to copper losses (resistance in the windings) and iron losses (hysteresis and eddy currents in the core). These losses generate heat and reduce the overall efficiency of the transformer.
Conclusion
I hope this explanation helps you understand how transformers work. This knowledge can be empowering, especially when dealing with electrical systems and home safety. Please leave a comment below and let me know what you think! You can also share this with your friends and check out more detailed information at https://homesafetools.com/.
