Cable Glands: Choosing & Installing the Right One for Home Safety. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
hoosing the Right Cable Gland: A Comprehensive Guide
Let’s dive into selecting the perfect cable gland for your home safety needs. First, you need to consider cable diameter and cable type. Precise measurement is key; a cable gland that’s too small won’t provide proper sealing, while one that’s too large might not offer sufficient strain relief. Cable type also matters – armored cables, for instance, need glands designed to accommodate their extra protection. For example, a cable with a diameter of 8mm needs a cable gland with a minimum diameter of 10mm to allow for proper insertion and sealing. This ensures a secure and safe connection. Remember, a poorly fitting cable gland can compromise the entire system’s integrity.
Next up is the environment. Environmental factors like moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures are major considerations. This is where the IP rating steps in. The IP rating, short for Ingress Protection rating, is a two-digit code indicating a product’s level of sealing effectiveness against solid objects (the first digit) and liquids (the second digit). An IP67 rating, for instance, means the cable gland is totally dust-tight and protected against immersion in water. For a bathroom, an IP67 rated cable gland is a must! You wouldn’t want water leaking into your electrical system. However, for a less demanding location, a lower IP rating might suffice. Consider the specific risks and choose accordingly.
The material of your cable gland is also critical. Metal cable glands, such as those made from brass or stainless steel, are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for outdoor applications and more demanding environments. However, plastic cable glands, often made from PVC or nylon, offer a cost-effective alternative suitable for many indoor applications. Plastic cable glands also offer flexibility and are often lighter. The choice depends on the specific application and your budget. Consider a cable gland made of brass for superior corrosion resistance. Metal in general offers better protection against physical damage than plastic.
Then there’s strain relief. A cable gland needs to reliably protect your cable from pulling and bending, preventing damage and potential safety hazards. A good cable gland will distribute the strain effectively, preventing damage to the wires inside the cable. Moreover, think about safety standards and compliance. Ensuring your cable gland meets relevant safety standards is vital for peace of mind. Adherence to standards like UL or IEC certifications guarantees a safe and reliable product.
This information will help you select the right cable gland, protecting your home and ensuring compliance. Remember, the EAVs (Entity-Attribute-Value) that are crucial to keep in mind are: Cable Gland – Type – Compression, Cable Gland – Material – Brass, Cable Gland – IP Rating – IP68, and Cable – Diameter – 10mm. These EAVs will guide your selection process. The EREs (Entity, Relation, Entity) to keep in mind are Cable Gland, ISUSEDFOR, Cable Protection, Cable Gland, HASRATING, IP67, and Cable, CONNECTEDTO, Enclosure. These illustrate the connections and relationships between different elements in your home’s electrical system. Finally, consider the semantic triples like Cable Gland, is a type of, Connector, Cable Gland, provides, Strain Relief, and Cable Gland, protects against, Water Ingress.
Remember, choosing the wrong cable gland can lead to serious safety issues. So take the time to understand these key aspects and make an informed decision.
Understanding Cable Gland Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Installing a cable gland might seem simple, but improper installation can negate all its protective benefits. Firstly, prepare your cable meticulously. Properly stripping the cable sheath and ensuring a clean entry point is essential for a secure and effective seal. Neglecting this can lead to water ingress or other environmental issues.
Next, carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific cable gland. Generally, you’ll insert the cable into the cable gland, tighten the gland nut, and ensure the cable is securely seated. Over-tightening can damage the cable, and under-tightening compromises the seal. Use the correct tools to achieve the correct torque – using a wrench designed for the job is critical. Too much or too little pressure can compromise the cable gland’s effectiveness.
After installation, a thorough visual inspection is vital. Check the seal for any visible signs of leaks, damage, or weaknesses. Look for obvious damage or abnormalities. If everything looks good, you’re ready to go! This simple step helps prevent future problems.
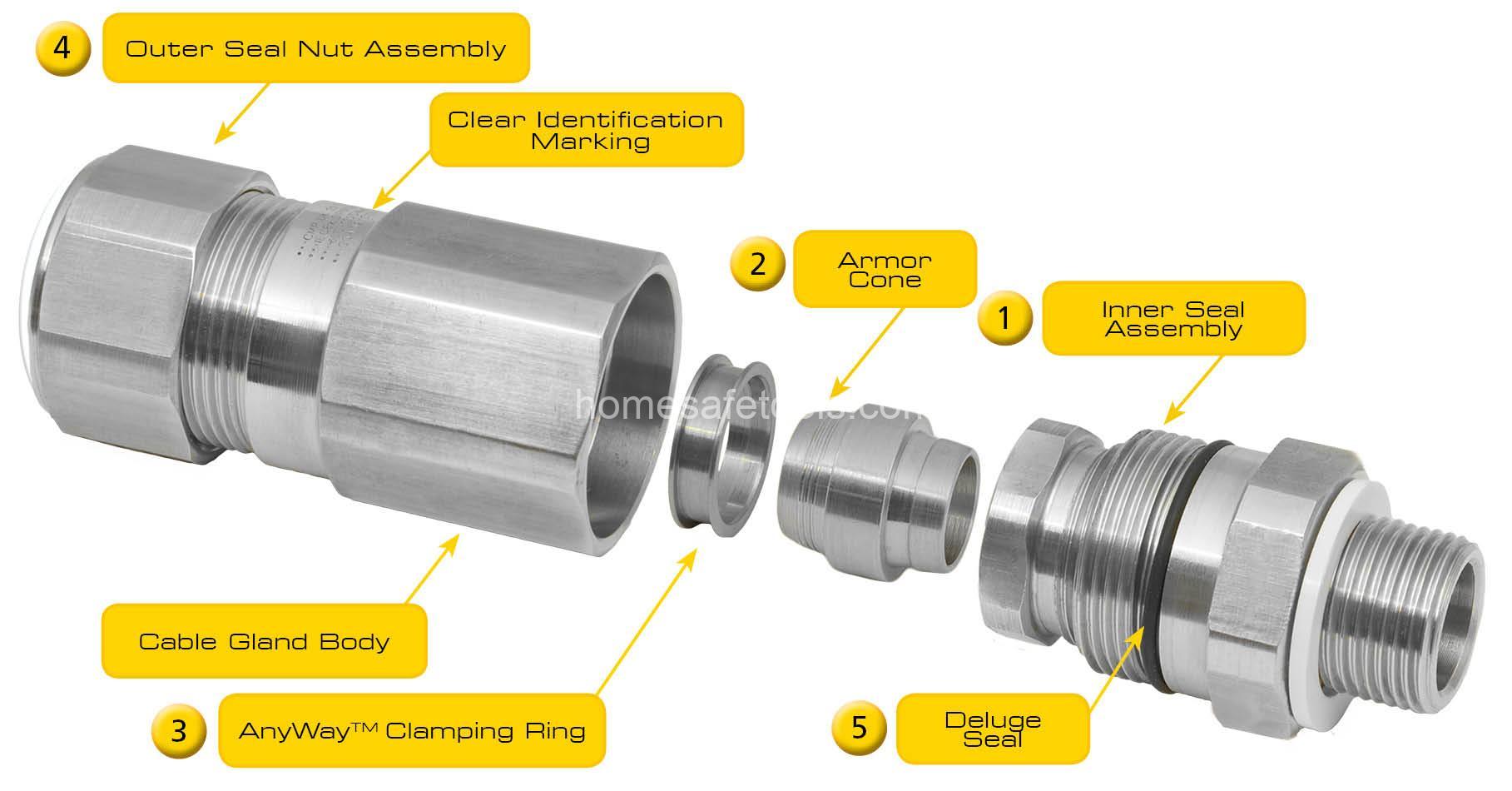
Types of Cable Glands and Their Applications
Several cable gland types exist, each suited to specific needs. Compression glands are the most common, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They work by compressing a sealing ring around the cable to create a watertight seal. Compression/swaging glands offer enhanced sealing capabilities, particularly useful in demanding environments. For the ultimate protection against harsh conditions, bonded glands provide superior sealing and durability, often exceeding standard IP ratings.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular inspection is key. Visually inspect your cable glands periodically to identify any issues like cracks, loose connections, or signs of water ingress. Early detection prevents larger, more costly problems. If you notice any signs of damage or deterioration, replace the cable gland immediately. Don’t delay, and remember safety always comes first.
Cable Gland Safety and Regulations
Understanding safety regulations is paramount. Ensure your chosen cable gland complies with all relevant safety standards for your region. This ensures a safe electrical environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a cable gland?
A cable gland serves several crucial purposes, primarily to protect electrical cables entering enclosures from environmental hazards (water, dust, etc.), provide strain relief to prevent cable damage, and ensure electrical safety by maintaining proper grounding.
How do I determine the correct IP rating for my needs?
The choice of IP rating depends entirely on the environment. Indoor applications might only require an IP65 rating, while outdoor or hazardous locations often mandate higher ratings like IP67 or even IP68. Consult the relevant standards and manufacturer specifications for detailed guidance.
What happens if I over-tighten a cable gland?
Over-tightening can damage the cable itself, potentially leading to short circuits or other safety hazards. It can also compromise the seal, rendering the cable gland ineffective.
Can I reuse a cable gland?
It’s generally not recommended to reuse a cable gland, especially after it’s been installed. The sealing mechanism might be compromised, decreasing its protective capabilities. Replacing with a new cable gland ensures optimum safety.
What should I do if I detect a leak around a cable gland?
A leak indicates a compromise in the seal. The cable gland should be immediately replaced to prevent water damage and potential electrical hazards.
Conclusion
Selecting and installing the right cable gland is critical for home safety. By following the guidelines outlined here, you can confidently protect your home’s electrical system. For more in-depth information and a wider selection of home safety tools, visit my website at https://homesafetools.com. I encourage you to leave comments, share this post, and check out our other articles for more helpful tips.
