Diodes: How They Work & Their Uses in Home Safety Tools. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
ow a Diode Works: Understanding Unidirectional Current Flow
Let’s start with the basics. A diode is a semiconductor device – a tiny component that only allows electricity to flow in one direction. Think of it like a one-way valve for electricity. This unidirectional property is key to its many applications. Now, how does it achieve this? It all comes down to the p-n junction.
The p-n junction is formed by joining two types of semiconductor material: p-type and n-type. P-type material has an excess of “holes” (positive charge carriers), while n-type material has an excess of electrons (negative charge carriers). When these materials meet, a depletion region forms – a zone where few charge carriers exist.
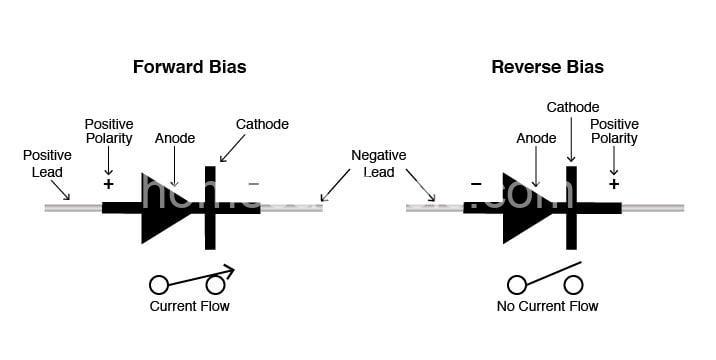
When you apply a forward bias voltage (positive to the p-side, negative to the n-side), the depletion region shrinks, allowing electrons to flow freely from the n-side to the p-side, and holes to flow in the opposite direction. This is like opening the one-way valve, allowing a current to flow. The current flows readily, but there’s a small voltage drop – typically around 0.7 volts for a silicon diode – across the junction.
On the other hand, applying a reverse bias voltage (negative to the p-side, positive to the n-side) widens the depletion region, significantly impeding current flow. It’s like closing the valve tightly; only a tiny leakage current can pass. This unidirectional behavior makes the diode a fundamental building block in many electronic circuits. A key aspect to consider is the reverse breakdown voltage. If you apply a sufficiently large reverse bias voltage, the diode will break down, and a large current may flow, potentially damaging the component. Understanding this limit is crucial in circuit design.
To visualize this, imagine a river flowing. In forward bias, the river flows freely through a wide channel. In reverse bias, the channel is extremely narrow, nearly blocking the flow. The I-V characteristic curve, a graph plotting current against voltage, provides a visual representation of this behavior.
Types of Diodes and Their Applications
Different types of diodes are optimized for specific tasks. Rectifier diodes, for example, are essential for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) – crucial for many home safety devices that require a stable DC power supply. Zener diodes maintain a constant voltage across themselves, regardless of current fluctuations, offering excellent voltage regulation. LEDs (light-emitting diodes) produce light when current flows through them. They’re commonly used in indicator lights on smoke detectors and other safety equipment. Finally, Schottky diodes are known for their fast switching speeds, making them suitable for high-frequency applications. Each type has its own unique strengths, making them versatile components across electronics. Consider the diverse applications of these diodes; they are far more common than you think!
Diode Applications in Electronics: Rectification, Protection, and More
Diodes play crucial roles in numerous applications found in various home safety products. Their primary function is rectification, the conversion of AC to DC. This is essential for powering many devices, ensuring they receive a steady voltage. Power supplies in smoke detectors, carbon monoxide detectors, and security systems rely heavily on this diode function.
Beyond rectification, diodes offer valuable protection against voltage surges and spikes. They act as safeguards for sensitive components, preventing damage from sudden voltage fluctuations that often occur on AC mains. In fact, a surge protector is likely using diodes to shunt excess voltage to the ground safely.
Diodes are also used for switching applications; acting as electronic switches that control the flow of current in various circuits. This ability finds applications in sophisticated control systems and timers found in some home safety systems. They even enable signal processing in more advanced systems, modifying and shaping electrical signals for specific purposes. In short, diodes are integral parts of modern home safety technologies, improving reliability and performance.
Key Characteristics of Diodes: Forward Bias, Reverse Bias, and Breakdown Voltage
Let’s delve deeper into the crucial characteristics of diodes that influence their functionality within the circuits of your home safety devices. Forward bias, as previously discussed, is the condition where the diode allows current to flow readily. A key factor to consider here is the forward voltage drop, which is the voltage difference across the diode when conducting current. This voltage varies depending on the type of diode.
Conversely, reverse bias is the state where the diode blocks current flow. Even in reverse bias, a minute amount of leakage current can pass, which can be ignored in most calculations. However, exceeding the reverse breakdown voltage can cause a significant and potentially damaging current to flow through the diode, therefore choosing the right diode for a project is always important. This is a crucial specification that must be considered during the design of any electronic circuit involving diodes.
Frequently Asked Questions about Diodes
What are the main differences between various diode types?
Different diode types have different characteristics, such as their forward voltage drop, switching speed, and maximum reverse voltage. Choosing the appropriate type is crucial for the specific application. For instance, a high-speed Schottky diode would be suitable for a high-frequency circuit whereas a standard rectifier diode would be the better option for simple AC to DC rectification.
How can I identify a diode in a circuit?
Diodes are usually identified by their markings, which will generally indicate their type and polarity. Some markings are more distinct than others but you should always take care when reading any markings to ensure you are not shorting any circuitry in the process.
How do diodes protect circuits from voltage surges?
Diodes act as one-way valves, diverting excessive voltage to ground, protecting sensitive components from damage. They are often included in circuits as a protection measure against sudden spikes.
Are diodes used in smart home devices?
Yes, diodes are integral to many smart home devices, contributing to functionality, power regulation, and signal processing. Their versatility makes them essential for a wide array of applications within the modern smart home.
Conclusion
Understanding the function of a diode is crucial for anyone interested in electronics and home safety. From rectification to surge protection, these versatile components significantly impact device performance and reliability. For more information on home safety tools and related topics, feel free to check out my website, https://homesafetools.com. Leave a comment, share this article, or explore more of my content for a deeper dive. Thanks for reading, and stay safe! – John Amrry
