Generator Safety Guide: Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning & Electrical Hazards. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
nderstanding Generator Safety Fundamentals
Using a generator can be a lifesaver during power outages, but it’s crucial to understand the inherent risks. Improper use can lead to serious consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, which is often fatal, and electrical hazards, which can cause severe injury or death. Let’s break down these crucial safety aspects.
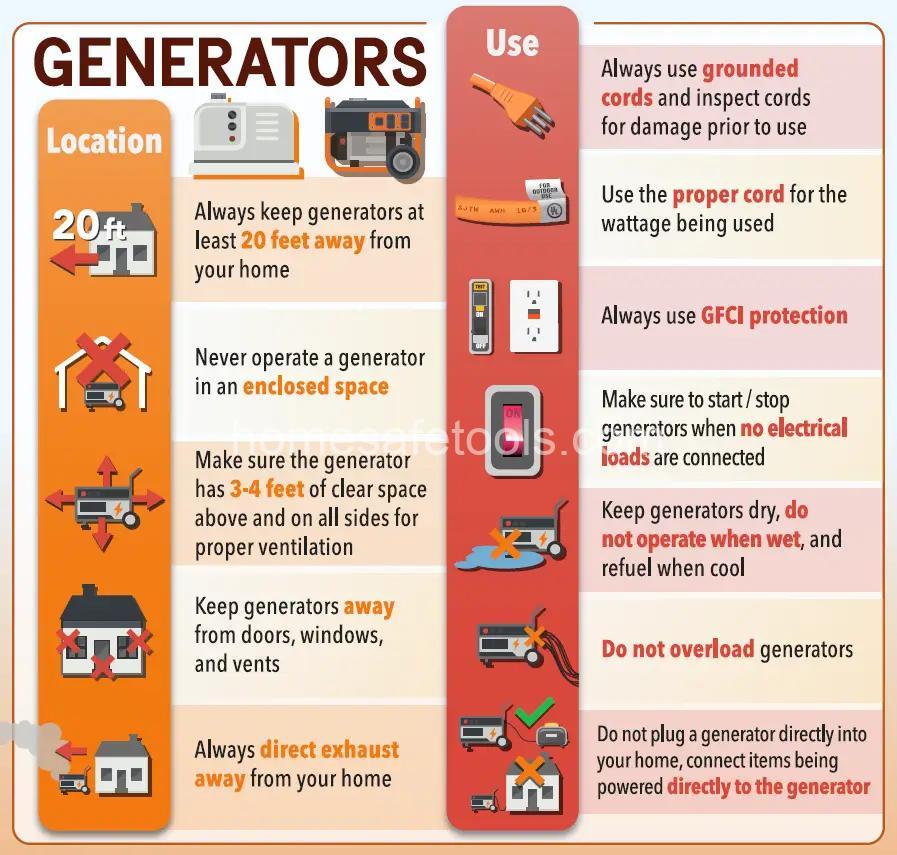
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: This invisible, odorless gas is produced when a generator burns fuel incompletely. Breathing it in can cause dizziness, headache, nausea, and even death. The most important safety rule is never to operate a generator indoors, including garages, basements, or sheds, even with the door open. The gas can easily accumulate, leading to dangerous levels. Always use your generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area, at least 20 feet away from windows, doors, and vents. Consider investing in a carbon monoxide detector to alert you to dangerous levels of the gas. Regularly checking the exhaust for unusual coloration or excessive soot buildup is another safety measure you can take.
Furthermore, make sure the area where you place your generator is flat and stable to prevent tipping. Tip-overs can not only damage your generator but also disrupt proper airflow, increasing the risk of carbon monoxide buildup. Maintaining a clear and unobstructed area around the generator, free from flammable materials and debris, is vital for preventing fire hazards.
Electrical Hazards: Generators produce high voltage electricity, so handling them improperly can result in severe electric shock. Always ensure that your hands are dry before operating the generator. If they are not dry, your risk of electric shock increases exponentially. Use insulated tools when working with the generator or its connections. Never touch exposed wires or attempt repairs without proper training. Using a properly grounded generator and connecting it to GFCI-protected outlets are crucial steps in mitigating electrical risks. GFCI protection shuts off power if it detects an imbalance, preventing shocks. Remember to unplug all equipment from the generator before performing any maintenance or repairs. Don’t overload the generator’s circuits – exceeding its capacity can overheat components and increase the risk of both electric shock and fire.
Fire Hazards: Gasoline is highly flammable, and improper handling poses a significant fire risk. Store fuel in approved, clearly marked containers away from the generator and sources of ignition. Avoid spilling gasoline, and never refill the tank while the generator is running. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the generator of any debris or loose parts, will also help reduce the risks of fire. The accumulation of debris such as leaves or twigs near the generator could easily catch fire from its hot engine.
Understanding these fundamental risks is the first step toward safe generator use. Remember, prevention is key.
Choosing and Setting Up Your Generator
Selecting the appropriate generator and installing it correctly significantly reduces the risk of accidents. Let’s explore how to make informed choices and set up your generator safely.
Selecting the Right Generator: Generators come in various sizes and types. You’ll need to determine your power requirements—the total wattage of all appliances you plan to run—before purchasing a generator. Underestimating your needs can lead to overloading and damage, so it’s better to slightly overestimate your power needs. Inverter generators are quieter and more fuel-efficient, but perhaps pricier. Standby generators offer automatic power backup, ideal for homes, but require professional installation. Portable generators are great for smaller jobs and are typically easy to maintain. Consider the safety features offered—look for features like low-oil shutdown, automatic voltage regulation, and GFCI protection. These features significantly reduce the risks of damage and accidents.
Safe Installation: Choose a level, stable surface for your generator, ensuring it’s on firm ground, away from flammable materials and dry vegetation. Remember, proper ventilation is paramount; position the generator far from windows, doors, and vents—at least 20 feet away is generally recommended. A well-ventilated space is vital for proper airflow and safe dissipation of the generated heat and exhaust fumes. Ensure the generator is sufficiently far away from structures such as your house or sheds. Use heavy-duty extension cords rated for the generator’s output, and never overload them. Overloading can cause overheating and fire.
Connecting Appliances: When connecting appliances, always start with the most important items and prioritize them based on their energy consumption. This means starting with the devices requiring the most power before adding any additional appliances. Ensure that the total wattage of the connected devices does not exceed the generator’s rated output capacity. This is crucial for preventing overloading, which can lead to overheating and potential equipment failure.
Operating Your Generator Safely
Safe operation minimizes risks. Let’s cover starting, monitoring, and shutting down.
Starting and Shutting Down: Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Check the oil and fuel levels before starting. Keep children and pets away from the generator during operation. When shutting down, allow the generator to cool down before covering or storing it.
Monitoring Operation: Regularly check the generator for any unusual sounds, smells (such as burning plastic), excessive vibrations, or overheating. If you notice anything unusual, shut down the generator immediately and contact a qualified technician.
Fuel Handling: Only use the type and grade of fuel specified in the manufacturer’s instructions. Always store gasoline in approved containers, away from ignition sources. Refuel only when the generator is turned off and cooled down, avoiding spills. Use a funnel to minimize spills and keep the area around the generator clean.
FAQs about How to Safely Use a Generator?
What are the most common causes of generator-related accidents?
The most common causes of accidents include carbon monoxide poisoning (from indoor operation), electrical shock (from improper grounding and handling), and fires (from fuel spills and overloaded circuits).
How can I prevent carbon monoxide poisoning when using a generator?
Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces. Ensure adequate ventilation around the generator (at least 20 feet from windows and doors). Use a carbon monoxide detector for added safety.
What type of extension cord should I use with a generator?
Use heavy-duty, weather-resistant extension cords rated for the generator’s output and the total amperage of the connected appliances. Never overload the extension cord.
How do I know if my generator is overloaded?
Overloading can cause the generator to overheat, the engine to stall, or the circuit breakers to trip. If you notice these symptoms, unplug some appliances and try again. Never attempt to increase the generator’s capacity by bypassing its safety features.
How often should I perform generator maintenance?
Consult your owner’s manual for recommended maintenance schedules. Regularly check oil levels, fuel lines, air filters, spark plugs, and the overall condition of the generator.
Conclusion
Using a generator safely requires diligence and adherence to best practices. By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risks of accidents and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with knowing you’re operating your generator responsibly. For more home safety tips and advice, visit my website at https://homesafetools.com. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below! Let’s keep each other safe! -John Amrry
