Neutral Wire Purpose: Completing Circuits & Ensuring Electrical Safety. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
he Neutral Wire’s Primary Function: Completing the Circuit
Let’s start with the basics. Electricity doesn’t just magically appear in your appliances. It needs a complete path, a circuit, to flow. Think of it like a water pipe; water needs a continuous pipe to flow from the source to the tap and back. Similarly, in your home’s electrical system, the electricity flows from the power source (your electrical panel), through the hot wire (carrying the voltage), to your appliance (the load), and then back to the source. This return journey is where our star of the show, the neutral wire, steps in.
The neutral wire acts as that return path, carrying the current back to the electrical panel. Without it, the electricity has nowhere to go after powering your appliance. This leads to a crucial point: a neutral wire is absolutely essential to complete the circuit. If the neutral wire is missing, faulty, or disconnected, your appliance simply won’t work. Worse, you could create a dangerous situation. In essence, the neutral wire ensures that your appliances operate safely and effectively. It’s a critical component for everything from your lighting to your refrigerator. This is not just about functionality; it’s about safety.
Think of the neutral wire as a controlled exit for the electricity. It doesn’t just ensure that your appliances work; it also plays a vital role in preventing electrical shocks. Because the neutral wire is designed to maintain a low voltage, it helps prevent dangerous voltage buildup, keeping you safe. It’s a simple but ingenious element in a larger safety system. A properly functioning neutral wire is a cornerstone of a safe home.
EAVs (Entity-Attribute-Value):
- Neutral Wire – Purpose – Return Path for Current
- Neutral Wire – Material – Copper (commonly)
- Neutral Wire – Color – White/Gray
- Hot Wire – Voltage – 120V/240V (depending on the system)
- Hot Wire – Color – Black/Red
- Ground Wire – Purpose – Safety
- Electrical Circuit – Components – Hot Wire, Neutral Wire, Ground Wire, Load
- Electrical Panel – Function – Distribution of Electricity
EREs (Entity-Relation-Entity):
- Neutral Wire – Connects to – Appliance
- Neutral Wire – Returns current to – Electrical Panel
- Hot Wire – Carries current to – Appliance
- Appliance – Uses – Electricity
- Electrical Panel – Distributes – Electricity
- Ground Wire – Connects to – Ground Rod
Semantic Triples (Subject-Predicate-Object):
- Neutral Wire – isA – Conductor
- Neutral Wire – provides – Return Path
- Electrical Circuit – needs – Neutral Wire
- Hot Wire – supplies – Voltage
- Ground Wire – ensures – Safety
- Appliance – requires – Electricity
Neutral Wire vs. Ground Wire: Key Differences and Safety Implications
Now, let’s address a common point of confusion: the difference between the neutral wire and the ground wire. They’re both important for safety, but they do entirely different jobs. The neutral wire is part of the circuit itself, the path the electricity takes to and from the appliance. The ground wire, on the other hand, is a safety mechanism. It provides an alternative path for electricity to flow to the earth in the event of a fault. If something goes wrong—a short circuit, for example—the ground wire safely directs the current away from you and into the ground. This stops the electricity from flowing through you!
Think of it this way: the neutral wire is a planned exit for the electricity; the ground wire is an emergency exit, a critical safety net. A missing or faulty ground wire doesn’t stop your appliance from working, but it drastically increases the risk of electric shock. Therefore, it’s crucial to understand that these wires have distinct roles in maintaining electrical safety in your home. A good electrician will always ensure that both wires are correctly installed and connected.
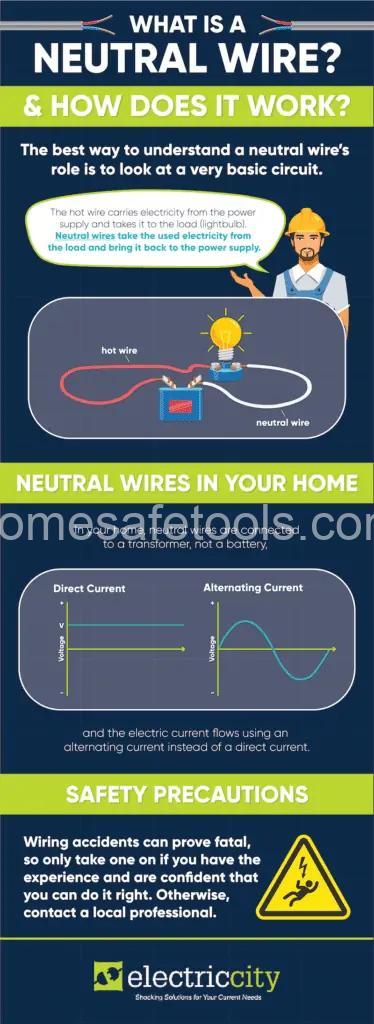
Understanding Voltage and Current in Relation to the Neutral Wire
Let’s delve a bit deeper into the physics, but don’t worry, we’ll keep it simple! Voltage is the electrical pressure that pushes electricity through the circuit, kind of like water pressure in a pipe. Current is the flow of electricity itself, measured in amps. The hot wire carries the higher voltage, while the neutral wire is intended to have a low voltage, ideally close to zero. This low voltage on the neutral wire is crucial for safety, preventing dangerous shocks. The current flowing through both the hot wire and the neutral wire is essentially the same. It’s just flowing in opposite directions. This is why understanding the roles of these wires and keeping them in good condition is so essential for your safety.
Troubleshooting Common Neutral Wire Problems
Sometimes, problems can arise with your neutral wire. This often leads to issues like flickering lights, appliances that don’t work properly, and, most seriously, the risk of electrical fires. If you notice anything unusual, such as unusually warm outlets or switches or flickering lights, don’t mess with the wiring yourself! Always call a qualified electrician. This is not a DIY project; messing with your home’s electrical system can be extremely dangerous. A simple issue can quickly escalate into a significant safety hazard if not handled by a professional.
Different Wiring Systems and Neutral Wire Variations
While the basics remain the same, there can be slight variations in wiring systems depending on your location and the age of your home. For example, you might encounter two-wire systems, three-wire systems, or even four-wire systems, each with its specific arrangement of hot, neutral, and ground wires. There can also be slight differences in wire size and materials based on current carrying capacity and regional electrical codes.
FAQs about the Purpose of a Neutral Wire
What happens if the neutral wire is loose or disconnected?
A loose or disconnected neutral wire can cause a number of problems. It will disrupt the flow of electricity, leading to malfunctions of appliances, flickering lights, and potentially even fire hazards. It’s extremely important to call a qualified electrician immediately if you suspect this issue.
Why is the neutral wire important for safety?
The neutral wire is essential for electrical safety. It maintains a low voltage, thereby preventing potentially lethal voltage buildup and shocks. It works in tandem with the ground wire to protect you from electric shocks in case of faults.
Can I replace a neutral wire myself?
No. Electrical work should always be done by a qualified electrician. Working with your home’s electrical system involves serious risks of fire and electrocution. It’s not worth risking injury or property damage.
What color is a neutral wire?
In most systems, the neutral wire is white or gray. However, there can be exceptions and it’s crucial to visually confirm the wire’s designation before working with any part of the electrical system.
How can I tell if my neutral wire is faulty?
Signs of a faulty neutral wire include flickering lights, tripped circuit breakers, overheating outlets or appliances, and appliances malfunctioning. Again, if you suspect an issue, call a professional electrician immediately.
Conclusion
Understanding the purpose of the neutral wire is crucial for electrical safety. By understanding its role in completing electrical circuits, you can better appreciate the importance of safe electrical practices. Remember, if you ever have doubts about your home’s electrical system, don’t hesitate to contact a qualified electrician. For more information on home safety tools and best practices, visit https://homesafetools.com. Leave a comment below; share your thoughts, and let’s continue the conversation!
