Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Power: A Complete Guide. In today’s article, homesafetools.com will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
nderstanding Three-Phase Power: A Deeper Dive
Three-phase power, unlike its single-phase counterpart, uses three separate alternating current waveforms, each 120 degrees out of phase with the others. This seemingly small difference has enormous implications for power delivery and application. Imagine it as three separate water pipes, each delivering water at slightly different times to create a continuous, powerful flow. That’s essentially how three-phase power works, providing a much smoother and more efficient energy supply than its single-phase cousin. This even flow reduces power fluctuations, leading to more consistent performance of equipment. You won’t find this even flow in single-phase systems, which leads to a less consistent supply of power. The consistent flow is critical for many high-power applications.
One of the key advantages of three-phase power is its significantly higher power capacity. Because it uses three phases instead of just one, it can deliver far more power for the same amount of wire and infrastructure. This is why you’ll find three-phase power extensively utilized in industries such as manufacturing, where heavy machinery requires substantial electrical power to operate. Think of large motors driving assembly lines or powerful compressors used in various industrial processes. These machines simply wouldn’t function efficiently, or at all, on single-phase power. The difference in power capacity is substantial, making it a necessity for industrial applications.
Furthermore, three-phase power is inherently more efficient. The balanced current flow minimizes losses and reduces the need for oversized wires, saving both material costs and energy. This translates to lower operating expenses and a smaller environmental footprint. This efficiency is a major factor contributing to the widespread adoption of three-phase power systems in industrial settings and large commercial buildings where energy savings are paramount.
The applications of three-phase power are vast, ranging from powering industrial machinery and large commercial buildings to the very backbone of our national power grids. Almost any industrial process that requires a significant amount of power will use three-phase power for its reliability, efficiency, and high power delivery. This consistent and powerful flow of energy underpins the functioning of countless industrial facilities around the world. It’s not just about power, it’s also about the consistent and reliable delivery of that power.
Moreover, three-phase power offers a much smoother power delivery compared to its single-phase counterpart. This is due to the constant flow of current, which minimizes voltage fluctuations and therefore ensures more stable operation of connected equipment. Less fluctuation equals fewer disruptions, less wear and tear on equipment, and ultimately, increased longevity for connected appliances and machinery.
Single-Phase Power Explained
Single-phase power, in its simplest form, consists of a single alternating current waveform delivered through two wires: a hot wire and a neutral wire. This simplicity makes it the ideal choice for most residential applications. Think of it as a single water pipe delivering water to your house; it’s straightforward and simple to manage. This setup is found in most homes worldwide, powering our everyday appliances.
Compared to three-phase power, single-phase power has a lower power capacity. It simply can’t deliver the same amount of power as three-phase, making it unsuitable for high-power applications. You wouldn’t want to try running a large industrial machine using just one phase of power; it would likely overheat and fail. It’s a simple system, and that simplicity comes with limitations.
However, the simplicity of single-phase power also means it’s less expensive to install and maintain compared to three-phase power. This is a crucial factor for many residential applications. The lower installation cost, combined with its suitability for lower power demands, makes it the most economical and practical choice for most households.
The typical applications for single-phase power are predominantly residential. It’s what powers your lights, appliances, and other everyday household items. These are usually items with relatively low power requirements. This system’s focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness within a manageable power range.
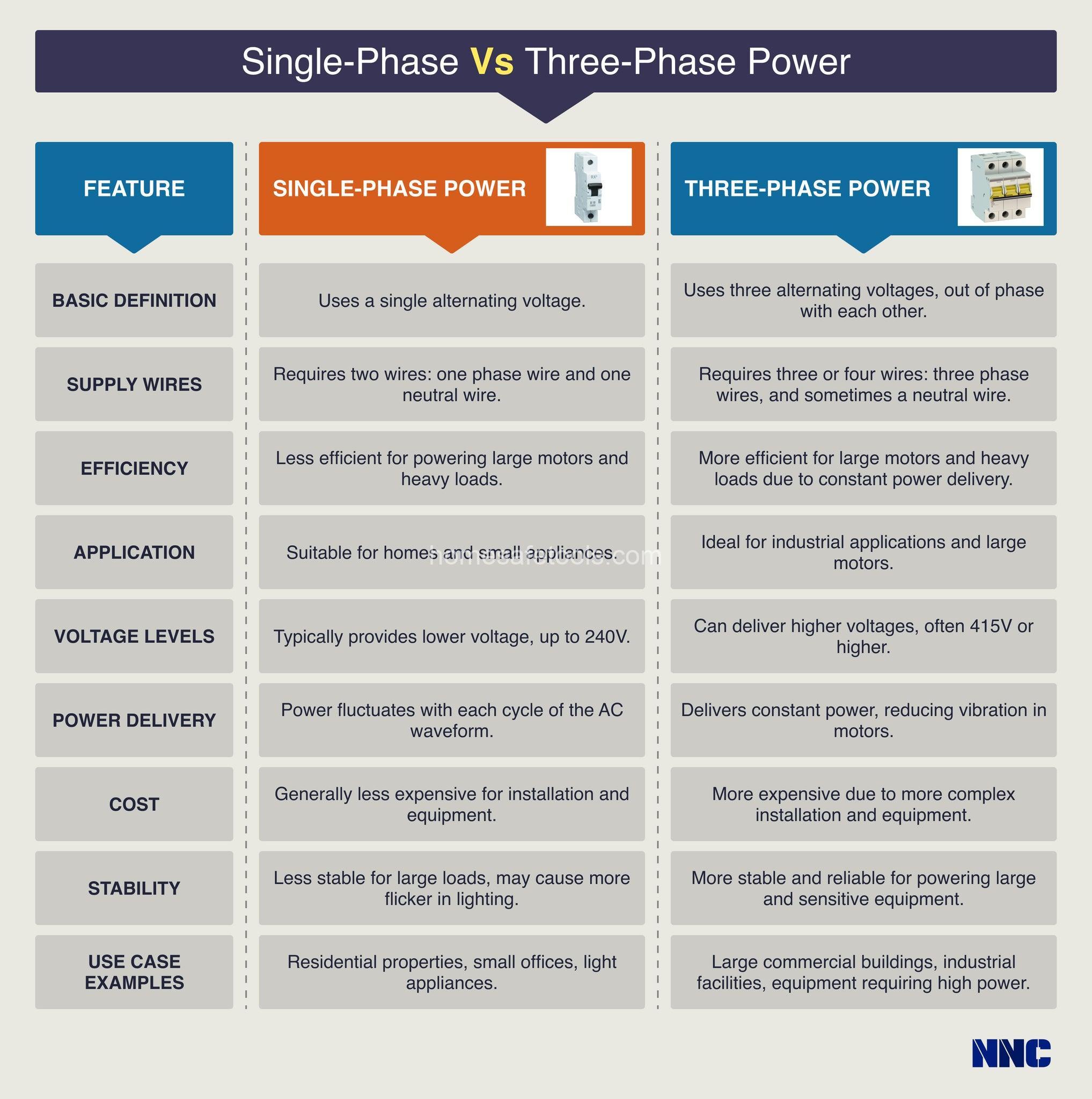
Head-to-Head Comparison: Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase
Let’s put these two power systems side-by-side to highlight their key differences:
| Feature | Single-Phase | Three-Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Phases | One | Three |
| Voltage | Typically 120V/240V (North America) | Typically 208V/480V (North America) |
| Current | Lower | Higher |
| Power Capacity | Lower | Much Higher |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | Lower initial installation and maintenance | Higher initial installation and maintenance |
| Applications | Residential, small appliances | Industrial, large buildings, power grids |
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between single-phase and three-phase power hinges on your specific energy requirements. For homes and small businesses with modest power needs, single-phase is usually sufficient. But for industrial applications, large commercial buildings, or situations demanding high power capacity, three-phase power is the only viable choice. The cost and complexity of three-phase systems become worthwhile only when the added power capacity is needed.
FAQs About Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
What are the main differences in voltage and current between single-phase and three-phase systems?
The key difference lies in the number of phases and their arrangement. Single-phase systems typically use 120V or 240V, while three-phase systems operate at higher voltages, such as 208V or 480V. This higher voltage in three-phase allows for higher power capacity with the same amperage, resulting in more efficient energy transmission. The higher current capacity of three-phase also allows for powering larger loads.
How does the efficiency of power transmission differ between the two systems?
Three-phase systems are significantly more efficient. The balanced nature of the three phases reduces power losses during transmission, leading to greater energy savings. Single-phase systems, on the other hand, experience higher losses due to the fluctuating current.
Why is three-phase power preferred for industrial applications?
Three-phase power’s higher power capacity, smoother power delivery, and greater efficiency make it ideal for heavy industrial machinery and large-scale operations. These applications demand consistent, high levels of power that a single-phase system cannot reliably provide.
Can I convert my home’s single-phase power to three-phase?
This is generally possible, but it’s a significant undertaking that requires professional electrical work and potentially upgrades to your home’s electrical infrastructure. The cost and complexity of such a conversion often outweigh the benefits unless there’s a very specific need for a major increase in power capacity.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase power is crucial for making informed decisions about your electrical needs. Whether it’s for your home or a larger project, choosing the right system is key for both efficiency and safety. Got questions? Let’s discuss! Leave a comment below, share this with your friends, or explore more insightful content on home safety at https://homesafetools.com. Thanks for reading! John Amrry, homesafetools.com.
